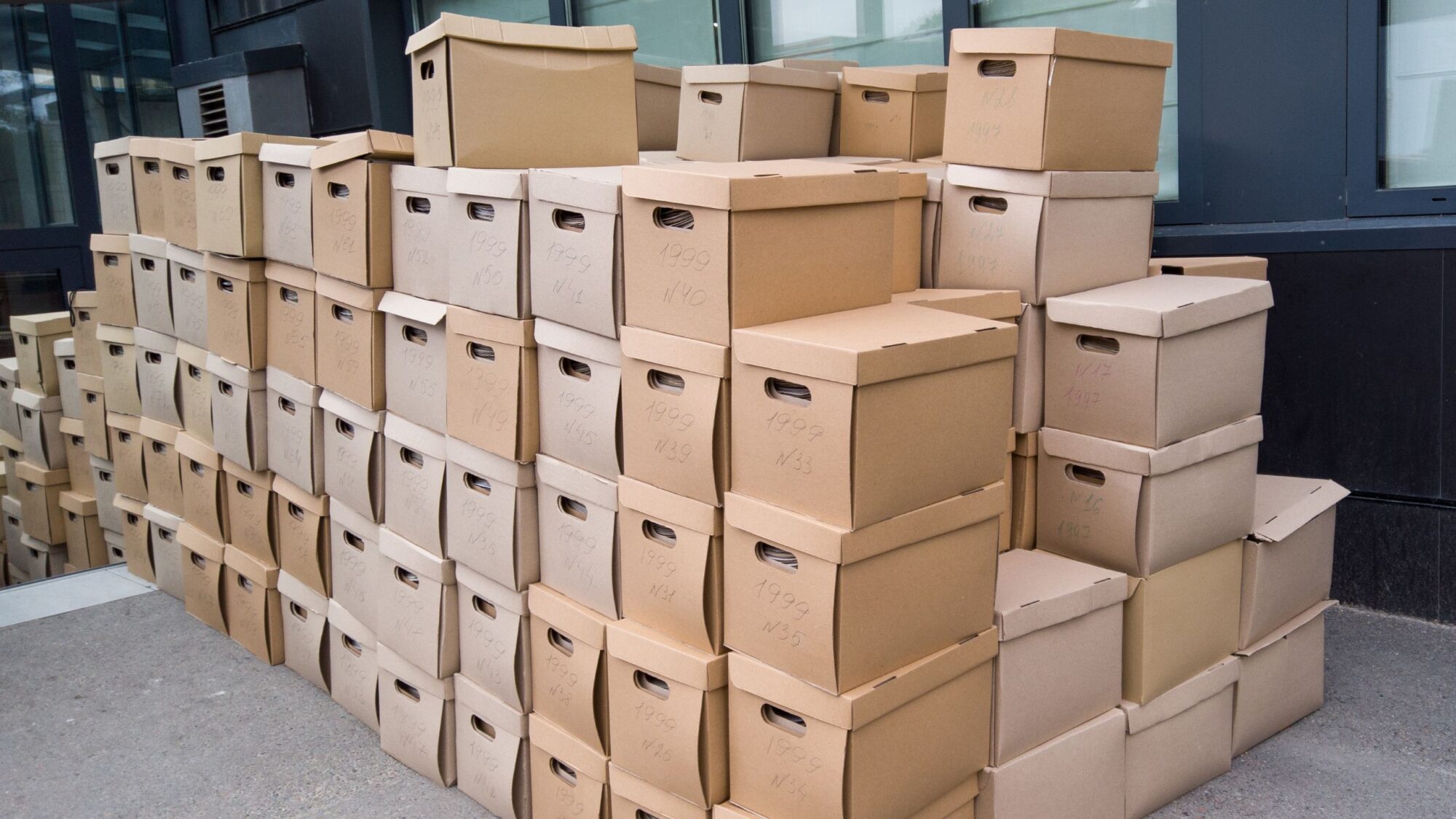
Our Services
Medical
Cariend’s expertise is in the handling and care of medical records. Cariend provides a comprehensive solution to handle all the compliance and workflow requirements that come with managing records after your healthcare facility is no longer operating.
Business
With the closing of a healthcare facility come business records with their own specialized procedures and retention policies. Cariend is uniquely equipped to handle business records with the same precision and skill we use with medical records.
Physical
Cariend has the flexibility and agility to manage all types of physical records, from paper to x-ray to pathology materials and electronic files. Our single solution allows all your records to be handled as one, creating ease during the closing of a facility and in perpetuity for your patients.
Our Evolution

Was founded to manage custodial records with the core belief that your records are your legacy, and they deserve the best possible treatment.
With decades of experience in the records information management (RIM) industry, we understand the many facets of closing your organization.
We can help you navigate the process, quickly removing the burden of managing your records.
The Cariend Continuum
Working with Cariend is simple. Just tell us what you have and how long the records need to be stored. Cariend will provide you with a comprehensive proposal, delivering cost certainty and compliance, ensuring peace of mind knowing patient requests will be well taken care of.
The Cariend Continuum is the process by which Cariend will handle the custodial transfer of your records. While each client situation is unique, the continuum describes the general process we follow.
1. Gather Information
Find out what types of records you have. Specifically, Cariend will need information about your data including the following:
- Types of Records
Cariend has the ability to store medical, financial, employment, and legal documents. - Quantity of Records
When estimating the amount of records you have, it’s best to think in terms of volume – the number of boxes, linear feet of physical records, or gigabytes of electronic records. Cariend can assist you in estimating the number of records. - Retention Policy
Retention requirements vary both by state and by record type. Your attorney or insurance provider should be able to confirm how long your records must be stored.
2. Propose Solution
Using the volume and retention information, Cariend will provide a comprehensive proposal, including upfront pricing with no hidden charges or surprises.
3. Transfer Records Custody
Upon signing an agreement, we consolidate the records in our secure storage facilities. Cariend manages both electronic and physical records. Physical records will be boxed for transport to our secure facility.
Cariend will create a custom solution for your electronic records to ensure a successful transition.
4. Notify Patients
We introduce you to our dedicated Release of Information team. You simply make this information available to those who are entitled to receive copies of the records throughout the statutory retention.
5. Release of Information
Going forward, Cariend manages the records entirely. Patients contact Cariend directly to request copies of their records via secure Release of Information. Valid requests will be transferred in a secure, HIPAA-compliant manner.
6. Secure Destruction
Once your required retention period has been met, Cariend securely destroys the records in a HIPAA-compliant manner upholding the nation’s most stringent standards for destruction.
Custodial Records Solutions are Second Nature to Us
Patient Care
The life cycle of your patients’ care and access to records will continue in perpetuity, long after your doors close. Our friendly and knowledgeable Release of Information (ROI) team will ensure your patients have timely, accurate, and secure access whenever there is a records request.
Cost Certainty
As an independent, employee-owned company, we are nimble mavericks. We conserve your resources without compromising the services we provide by creating customized solutions that meet your unique needs. And with an up-front fee structure, there are no surprise costs later – for you or your patients!
Compliance
Compliance is akin to the laws of nature – absolutes that will never be violated. As dedicated experts in the records information management (RIM) field, we provide the ability for you to simply walk away knowing records are managed in a way that minimizes risk, provides access in a secure manner, and maintains the industry’s highest compliance standards.
Common Mistakes
From years of experience, Cariend’s custodial records team frequently sees the same mistakes made by healthcare facilities closing.
Download our guide to learn about these common mistakes and how to avoid them.

Medical Records Retention by State
Click on your state in the map below for an explanation of the basics of medical records retention laws specific to your state. As always, the team at Cariend is standing by for any questions or further concerns about your state’s policy.
| Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians | Guidance for Doctors Only | ||
| Guidance for Hospitals Only | No guidance |
| Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians | |
| Guidance for Hospitals Only | |
| Guidance for Doctors Only | |
| No guidance |
-
Alabama - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals: Alabama hospitals must keep patient records for a minimum of five (5) years after patient discharge. Minor patients’ records must be kept for five (5) years after they have reached adulthood.
Physicians: Private practices must keep records “as long as may be necessary to treat the patient and for medical and legal purposes.”
Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for medical records retention policy.
ALA. ADMIN. CODE r. 420-5-7-.13
https://bit.ly/3PXOkve -
Alaska - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: Alaska state law requires that hospitals retain records for seven (7) years following the release of the patient. Records concerning patients under the age of 19 must be kept for seven (7) years or until the patient reaches the age of 21, whichever is longer.
Physicians: Alaska does not offer medical records retention guidance for private practices. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for medical records retention policy.
ALASKA STAT. § 18.20.085
https://bit.ly/3vhwriQ -
Arizona - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals and Physicians: Arizona state statute covers retention policy for all medical care providers, including both hospitals and private practices. Adult medical records are kept for six (6) years; minor patient records are kept for six (6) years or until the patient reaches the age of 21, whichever is longer.
ARIZ. REV. STAT. ANN. § 12-2297
https://bit.ly/3ODpqzP -
Arkansas - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: Arkansas state law requires hospitals to keep records for ten (10) years following the last discharge of the patient, and in the case of minor patients, until two (2) years after the patient turns 18.
Physicians: Arkansas does not offer medical records retention guidance for private practices. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for medical records retention policy.
ARK. CODE R. § 007.05.17
https://bit.ly/3b6wPtP -
California - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: The California Code of Regulations mandates that hospitals keep patient records for seven (7) years following patient discharge, and in the case of minors, seven (7) years or one year after the patient turns 18.
Physicians: California does not offer medical records retention guidance for private practices. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for medical records retention policy.
22 CA ADC §70751
https://bit.ly/3BfKw47 -
Colorado - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: Colorado mandates that hospitals keep records for ten (10) years after the most recent patient care. In the case of minors, Colorado requires retention of records for ten (10) years following the patient turning 18.
Physicians: Colorado does not offer medical records retention guidance for private practices. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for medical records retention policy.
6 COLO. CODE REGS. § 1011-1: IV-8.102
https://bit.ly/3S0FnD3 -
Connecticut - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals: Connecticut law requires hospitals to keep records for ten (10) years after patient discharge.
Physicians: Private practices must keep records for seven (7) years after last date of treatment, or in the case of patient death, three (3) years.
CONN. AGENCIES REGS § 19-13-D3
https://bit.ly/3PFVODe -
Delaware - Guidance for Doctors Only
Hospitals: Delaware does not offer medical records retention guidance for hospitals. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for medical records retention policy.
Physicians: Delaware state codes require private practices to keep medical records for seven (7) years after the last entry date on the patient’s record.
DEL. CODE ANN. tit. 24 § 1761
https://bit.ly/3z9cDiW -
Florida - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals: The Florida Department of State mandates that public hospitals keep records for seven (7) years after the final entry into the patient’s records.
Physicians: Florida administrative codes require private practices keep patient records for five (5) years after final patient contact.
FLA. ADMIN. CODE ANN. r. 64B8-10.002
https://bit.ly/3vi2bEt -
Georgia - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals: Georgia code requires that hospitals keep records for five (5) years following the date of patient discharge, or in the case of minor patients, for five (5) years after the patient turns 18.
Physicians: Georgia code requires that private practices hold records for ten (10) years from the date the record item was created.
COMP. R. & REGS. § 111-8-40-.18
https://bit.ly/3PC6Nh7 -
Hawaii - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals and Physicians: Hawaii offers blanket guidance for all medical care providers. Full patient records should be kept for seven (7) years following last patient contact. For minors, records must be kept for seven (7) years following the patient’s 18th birthday.
HAW. REV. STAT. § 622-58
https://bit.ly/3OJJ25y -
Idaho - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: Public hospitals in Idaho must keep records and reports from clinical lab tests for five (5) years.
Physicians: Idaho offers no distinct records retention guidance for private practices. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for medical records retention policy.
IDAHO CODE ANN. § 39-1394
https://bit.ly/3BnratY -
Illinois - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: Illinois law requires hospitals keep patient records for ten (10) years after the discharge of the patient.
Physicians: Illinois offers limited guidance for private practices. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for medical records retention policy.
210 ILL. COMP. STAT. § 85/6.17
https://bit.ly/3OF9eho -
Indiana - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals and Physicians: Indiana requires medical records retention periods for seven (7) years for both hospitals and private practices.
IND. CODE § 16-39-7-1
https://bit.ly/3zzscSh -
Iowa - Guidance for Doctors Only
Hospitals: Iowa offers limited guidance for public hospitals. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for records retention policy.
Physicians: Iowa enforces a seven (7) year retention period from the date of last service for private practice medical records and one (1) year after a minor turns 18.
IOWA ADMIN. CODE R. 653-13.7
https://bit.ly/3PAT0r9 -
Kansas - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals and Physicians: Kansas requires both hospitals and private practices retain their records for ten (10) years after the patient’s discharge or final record entry. For minors, the same period or one (1) year beyond the patient’s 18th birthday applies, whichever is longer.
KAN. ADMIN. REGS. § 28-34-9a
https://bit.ly/3vi44Rz -
Kentucky - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: Kentucky requires that hospitals retain patient records for five (5) years following the discharge of the patient, or in the case of minors, for five (5) years or until the patient turns 21, whichever is longer.
Physicians: Kentucky offers no state guidance for medical records retention for private practices. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for records retention policy.
902 KY. ADMIN. REGS. 20:058
https://bit.ly/3JeLxeP -
Louisiana - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals: Louisiana requires hospitals keep their records for ten (10) years following the discharge of the patient.
Physicians: Private practices must retain records for six (6) years following the date a patient is last seen.
REV. STAT. ANN.§ 40:2144
https://bit.ly/3b2AJ77 -
Maine - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: Maine state codes require hospitals keep records for seven (7) years, or in the case of minor patients, until six (6) years after the patient turns 18.
Physicians: Maine state codes also mandate permanent retention for certain patient data, including x-ray reports. Maine does not offer specific guidance for private practices. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for records retention policy.
22 MRS §1711
https://bit.ly/3OAahzd -
Maryland - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals and Physicians: Maryland offers a standard retention period for both hospitals and private practices of five (5) years. In the case of minor patients, the period is five (5) years or three (3) years after the patient turns 18, whichever is longer.
CODE REGS. §10.01.16.04
https://bit.ly/3z4DMDA -
Massachusetts - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals: Massachusetts law requires that hospitals retain records for twenty (20) years after the discharge or final treatment of the patient.
Physicians: Massachusetts regulatory codes mandate a seven (7) year retention period for adult patients. For minor patients, the period is seven (7) years or until the patient turns 18, whichever is longer.
243 MASS. CODE REGS. § 2.07
https://bit.ly/3z2sOhK -
Michigan - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals and Physicians: Michigan law requires that both private practices and hospitals retain their records for seven (7) years from the date of the patient’s discharge or last treatment.
MICH. COMP. LAWS § 333.16213
https://bit.ly/3vivJBV -
Minnesota - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: For public hospitals, Minnesota requires mixed retention periods for varying types of records. Ultimately, hospitals must keep patient records for seven (7) years, or in the case of minors, for seven (7) years after the patient turns 18.
Physicians: Minnesota offers limited retention guidance for private practices. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for records retention policy or contact Cariend to learn more about retention policy in Minnesota.
MINN. STAT. § 145.32
https://bit.ly/3Pyda4S -
Mississippi - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: Mississippi enforces different retention periods for patient records depending on certain details about the patient. For adults discharged “in sound mind”, records must be held for ten (10) years. For deceased patients, records must be held for seven (7) years. For minor patients, records must be held for the period of minority plus seven (7) years, but not to exceed twenty-eight (28) years.
X-ray films and other graphic data must be retained for four (4) years.
Physicians: Mississippi offers limited retention guidance for private practices. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for records retention policy, or contact Cariend to learn more about retention policy in Mississippi.
MISS. CODE ANN. § 41-9-69
https://bit.ly/3PXV5Ny -
Missouri - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals: Missouri requires that public hospitals keep adult records for ten (10) years and minor patient records for ten (10) years, or until the patient turns 23.
Physicians: Private practices must keep records for seven (7) years following the last date of service.
REV. STAT. § 334.097
https://bit.ly/3z4HNIa -
Montana - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: Montana requires public hospitals retain a patient’s entire medical record for ten (10) years following discharge or patient death. For minors, the period is through the patient’s 18th birthday (or death, whichever earlier), plus ten (10) years.
Health care providers must also maintain records of existing health care information for one (1) year following receipt of authorization to disclose that information.
Physicians: Montana offers limited retention guidance for private practices. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for records retention policy.
MONT. CODE ANN. § 50-16-513
MONT. ADMIN. R. 37.106.402
https://bit.ly/3Be0Dzk
https://bit.ly/3S3Mmel -
Nebraska - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: Nebraska administrative codes require hospitals to retain records for ten (10) years, or in the case of minor patients, ten (10) years or until three (3) years after the patient turns 18.
Physicians: Nebraska offers limited retention guidance for private practices. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for records retention policy.
175 NEB. ADMIN CODE § 9-006
https://bit.ly/3BhT8qW -
Nevada - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals and Physicians: Nevada enforces the same retention period of five (5) years across both public and private institutions. In the case of minor patients, the period is for five (5) years following the patient’s 18th birthday.
NEV. REV. STAT. § 629.051
https://bit.ly/3zxqpNK -
New Hampshire - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals and Physicians: New Hampshire enforces the same retention period of seven (7) years after patient discharge for both hospitals and private practices. In the case of minors, the period is seven (7) years or until the patient reaches age 19, whichever is longer.
N.H. CODE ADMIN. R. ANN. He-P 802.20
https://bit.ly/3J76Kam -
New Jersey - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals: New Jersey requires hospitals to keep records for ten(10) years following patient discharge.
Physicians: Private practices must keep them for seven (7) years. New Jersey enforces unique retention periods for discharge summary sheets.
N.J. STAT. ANN. § 26:8-5:
https://bit.ly/2QUsycy -
New Mexico - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals: New Mexico requires hospitals retain records for a standard of ten (10) years after discharge. For minors, records must be retained until the patient reaches 21 years of age.
Physicians: Private practices must navigate existing Medicare laws and insurance mandates and add two (2) years to all requirements therein to meet state retention standards. This generally means at least ten (10) years from the date of the last treatment. Private practices must retain records for minor patients until the patient turns 21.
N.M. CODE R. § 16.10.17.10
https://bit.ly/3baEHdM -
New York - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals and Physicians: New York holds hospitals and private practices to the same retention standard of ten (10) years for adult patients. standards for minor patients. In the case of minor patients, the period is for six (6) years or until three (3) years after the patient turns 18. Deceased patient records must be held for six (6) years beyond the date of death.
N.Y. COMP. CODES R. & REGS. § 405.10
https://on.ny.gov/3ozbCM0 -
North Carolina - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: North Carolina requires that hospitals keep records for eleven (11) years following the last treatment of the patient, and in the case of minors, until the patient’s 30th birthday.
Physicians: North Carolina does not offer clear retention guidance for private practices. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for records retention policy.
10A N.C. ADMIN. CODE § 13B.3903
https://bit.ly/3PRKjrY -
North Dakota - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: North Dakota enforces a patient record retention period of ten (10) years for hospitals, and in the case of minor patients, ten (10) years or until the patient’s 21st birthday, whichever is longer.
Physicians: North Dakota does not offer direct medical records retention guidance to private practices. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for records retention policy.
N.D. ADMIN. CODE § 33-07-01.1-20
https://bit.ly/3z8E5NB -
Ohio - Guidance for Doctors Only
Hospitals: Ohio offers no direct guidance for medical records retention policy in the form of state law or code. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for records retention policy, or contact Cariend to learn more about retention policy in Ohio.
Physicians: The provider of a health care service must retain medical records for Medicaid patients for six (6) years from the date of discharge.
OHIO ADMIN. CODE § 2913.40
https://bit.ly/3J5LQZt -
Oklahoma - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: Oklahoma requires hospitals to keep records for five (5) years after the date the patient was last seen (or in the case of patient death, three (3) years). In the case of minor patients, records must be kept until their 21st birthday.
Physicians: Oklahoma offers limited medical records retention guidance for private practices. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for records retention policy.
OKLA. ADMIN. CODE § 310:667-19-14
https://bit.ly/3zuaDSH -
Oregon - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: Oregon requires that hospitals keep records for ten (10) years beyond the last date of patient treatment. Oregon also requires master patient records to be kept permanently.
Physicians: Oregon offers limited medical records retention guidance for private practices. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for records retention policy.
ADMIN. R. 333-505-0050
https://bit.ly/3vipoGB -
Pennsylvania - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals: Pennsylvania requires medical records be kept a minimum of seven (7) years following the discharge of a patient. If the patient is a minor, records shall be kept until the age of majority, and then for seven (7) years “or as long as the records of adult patients are maintained.” Essentially, hospitals must retain patient records for minors until the patient reaches age 25, or seven (7) years after a patient turns 18 years old.
Physicians: Pennsylvania requires private practices to retain adult patient records for a minimum of seven (7) years from the date of the last medical service. The medical records for a minor patient must be retained until one (1) year after the minor patient reaches majority, even if that means the physician retains the records for a period of more than seven (7) years.
28 PA. CODE § 115.23
https://bit.ly/3oDULrm
https://bit.ly/3S2TJCV -
Rhode Island - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospital and Physicians: Rhode Island requires that both hospitals and private practices keep records for five (5) years after the patient is discharged.
In the case of minor patients, hospitals must keep records for five (5) years after the patient turns 18.
Physicians must retain all medical records for seven (7) years.
31-5-41 R.I. CODE R. § 11.0
31-4-18 R.I. CODE R. § 27.0
https://bit.ly/3JbD9Nd -
South Carolina - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals: South Carolina requires that hospitals retain medical records for ten (10) years. In the case of minor patients, medical records must be retained until the patient turns 18 years old and the “period of election” passes. Functionally, this means when the patient turns 19.
Physicians: South Carolina requires physicians to retain medical records for at least ten (10) years for adult patients. Minor patient records must be held for thirteen (13) years. Minimum recordkeeping periods begin from the last date of treatment.
S.C. CODE ANN. § 44-115-120
S.C. CODE ANN. REGS. 61-16 § 1107
https://bit.ly/3vjuvGH
https://bit.ly/3vHIVkj
https://bit.ly/3S38NAt -
South Dakota - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals: South Dakota hospitals must keep records for ten years following the discharge or last care of the patient. In the case of minor patients, the retention period is ten years or until two (2) years after the patient turns 18, whichever is longer.
Physicians: South Dakota requires private practices to hold records until the point when records have become inactive or for which the whereabouts of the patient are unknown to the physician.
Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited or vague legal guidelines for records retention policy or contact Cariend to learn more about medical records retention in South Dakota.
S.D. ADMIN. R. 44:73:09:06
S.D. CODIFIED LAWS § 36-4-38
https://bit.ly/3Q3HVyF
https://bit.ly/3PPfBzQ -
Tennessee - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals and Physicians: Tennessee requires all medical care providers to adhere to a retention policy of ten (10) years for adult medical records. For minor patients, the period is ten (10) years or until the patient’s 19th birthday, whichever is longer.
TENN. COMP. R. & REGS. 1200-08-01-.06
TENN. COMP. R. & REGS. 0880-02-.15
TENN. CODE ANN. § 68-11-305
TENN. CODE ANN. § 68-11-307
https://bit.ly/3vknGok
https://bit.ly/3OxwYEg -
Texas - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals: Texas requires hospitals to keep patient records for ten (10) years following discharge, and in the case of minor patients, for ten (10) years or until the patient turns 20 years old, whichever is longer.
Physicians: Private practicing doctors in Texas must keep medical records for seven (7) years, and in the case of minor patients, for seven (7) years or until the patient reaches age 21, whichever is longer.
22 TEX. ADMIN. CODE § 165.1
TEX. HEALTH & SAFETY CODE § 241.103
https://bit.ly/3PV7wcQ
https://bit.ly/3ows7J1 -
Utah - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: Utah requires that hospitals keep patient records for seven (7) years, or in the case of minors, seven (7) years or until the minor patient turns 22, whichever is longer.
Physicians: Utah offers limited medical records retention guidance for private practices. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for records retention policy.
UTAH ADMIN. CODE §432-100-33
https://bit.ly/3b4T1Vj -
Vermont - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: Vermont requires hospitals to keep records for ten (10) years after patient discharge.
Physicians: Vermont offers limited medical records retention guidance for private practices. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for records retention policy.
12-5-14 VT. CODE R. §946
STAT. ANN. tit. 18 § 1905
https://bit.ly/3zEm9w1 -
Virginia - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals: For Virginia hospitals, the period is five (5) years, or in the case of minor patients, when the patient turns 23.
Physicians: For private practices, Virginia requires a retention period of six (6) years, or in the case of minor patients, six (6) years or until the patient reaches age 18 or becomes emancipated, whichever is longer.
18 VA. ADMIN. CODE § 85-20-26
12 VA. ADMIN. CODE § 5-410-370
https://bit.ly/3S3Yv32
https://bit.ly/3OAiF1D -
Washington - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: Washington requires hospitals keep their adult patient records for ten (10) years, and minor patient records for ten (10) years or until the patient reaches the age of 21, whichever is longer.
Physicians: Washington offers limited medical records retention guidance for private practices. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for records retention policy.
WASH. REV. CODE § 70.41.190
https://bit.ly/3PGu7dA -
West Virginia - No guidance
West Virginia offers no direct guidance for medical records retention policy in the form of state law or code. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for records retention policy, or contact Cariend to learn more about retention policy in West Virginia.
W.VA. CODE R. 64-12-7
-
Wisconsin - Guidance for Hospitals and Physicians
Hospitals and Physicians: Wisconsin requires all medical care providers follow the same retention standard of five (5) years past the date of last entry in the record.
WIS. ADMIN. CODE MED §21.03
WIS. ADMIN. CODE DHS §124.14
https://bit.ly/3za7bw8
https://bit.ly/3cKJMKn -
Wyoming - Guidance for Hospitals Only
Hospitals: Wyoming hospitals must retain patient medical records for three (3) years.
Physicians: Wyoming offers no direct guidance for private practice medical records retention policy in the form of state law or code. Consult LINK for more on what to do when your state offers limited legal guidelines for records retention policy or contact Cariend to learn more about retention policy in Wyoming.
WYO. STAT. ANN. § 35-2-606
Disclaimer: This map is designed to provide introductory insight into complex laws governing state medical records retention policy. This map should not be used for legal purposes, nor should it be used as the sole resource in forming or implementing an organizational retention policy. Please consult an attorney with specific legal issues related to medical records retention.
The information featured in this map is current as of July 2022 but can change in the future.